【Verl源码分析(二)】Verl中的数据流动
注意查看的是0.4.1.x版本的Verl代码:https://github.com/verl-project/verl/tree/v0.4.1.x
下面给出verl/trainer/ppo/ray_trainer.py中RayPPOTrainer.fit简化后的核心流程代码,也就是Verl中训练的核心流程,下面以此为核心从数据流动的视角进行介绍:
1 | |
数据流动
原始数据集处理
整体概览如下:
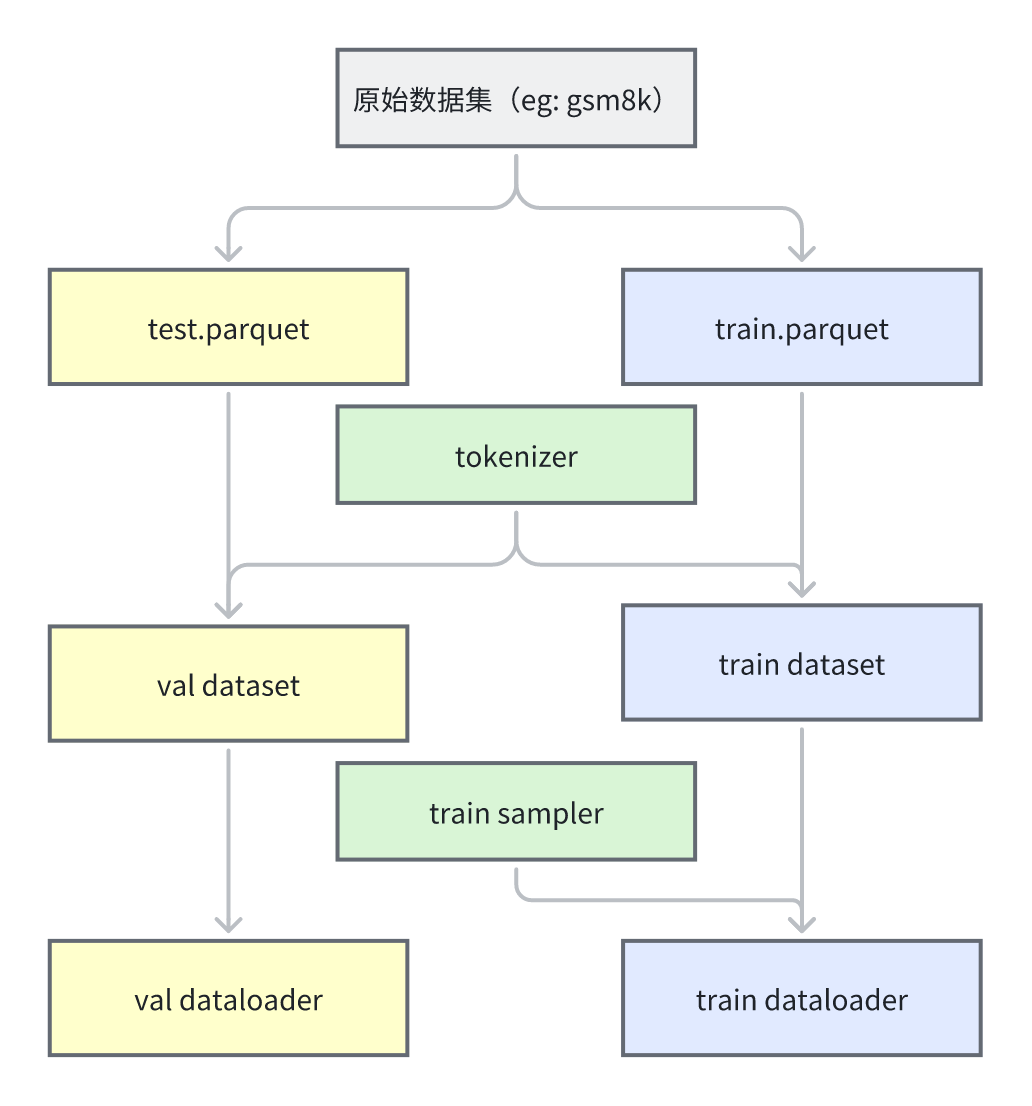
这里以经典的gsm8k数据集(https://huggingface.co/datasets/openai/gsm8k)为例,介绍Verl对其一开始做了什么处理。
gsm8k数据集分为训练集和测试集,每个数据集中包含2个字段,分别是question和answer,其中answer会以
####{最终答案}的形式来记录最终答案。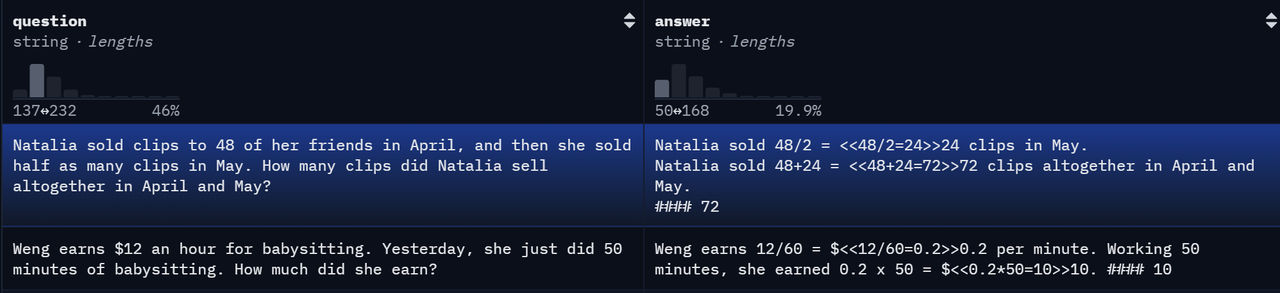
Verl提供了
examples/data_preprocess/gsm8k.py来处理该原始数据集,将其进行格式转换,最终存储为test.parquet和train.parquet。其核心处理是给每个问题后面添加了
Let\'s think step by step and output the final answer after "####".来引导模型用####{最终答案}的方式来输出。然后将其格式转化为了如下的样式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17data = {
"data_source": data_source,
"prompt": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": question,
}
],
"ability": "math",
"reward_model": {"style": "rule", "ground_truth": solution},
"extra_info": {
"split": split,
"index": idx,
"answer": answer_raw,
"question": question_raw,
},
}- 这里取其中一个问题为例进行介绍:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20{
"data_source": "openai/gsm8k",
"prompt": [
{
"content": "Natalia sold clips to 48 of her friends in April, and then she sold half as many clips in May. How many clips did Natalia sell altogether in April and May? Let\"s think step by step and output the final answer after "####".",
"role": "user"
}
],
"ability": "math",
"reward_model": {
"ground_truth": "72",
"style": "rule"
},
"extra_info": {
"answer": "Natalia sold 48/2 = <<48/2=24>>24 clips in May.\nNatalia sold 48+24 = <<48+24=72>>72 clips altogether in April and May.\n#### 72",
"index": 0,
"question": "Natalia sold clips to 48 of her friends in April, and then she sold half as many clips in May. How many clips did Natalia sell altogether in April and May?",
"split": "train"
}
}- 注意转换为
parquet格式的一个好处在于parquet是列存储的,其可以很方便地直接读取到某一属性的所有值。
进一步在训练前会进行数据的预处理将其转化为
train_dataloader与val_dataloader:首先分别读取
test.parquet和train.parquet,并分别包装为RLHFDataset(Dataset)类型的train_dataset和val_dataset,其主要作用是记录了一些关键配置,读取并保存对应的parquet文件以及tokenizer和多模态处理的processor然后再创建一个
train_sampler负责采样训练数据然后结合
train_dataset与train_sampler构建出一个torchdata.stateful_dataloader类型的train_dataloader,torchdata.stateful_dataloader类型的主要特点是可以从checkpoint中恢复上次数据读取的位置,从而保证数据采样的轨迹还是和之前相同。进一步的还会创建出
val_dataloader负责加载验证集数据
训练迭代中的数据处理
总体概览如下:
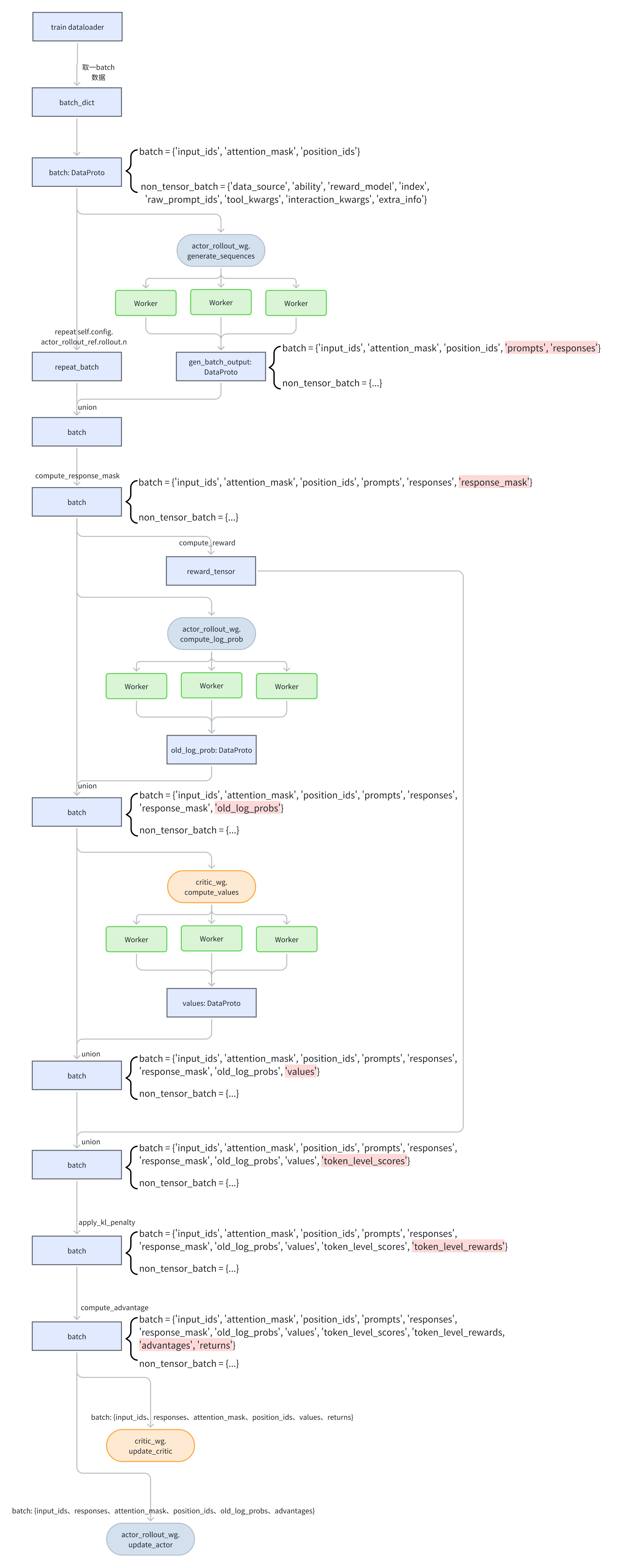
在训练迭代过程中会读取dataloader来获取数据进行训练与验证
- 在训练过程中读取
train_dataloader的相关代码如下:
1
2
3
4for epoch in range(self.config.trainer.total_epochs):
for batch_dict in self.train_dataloader:
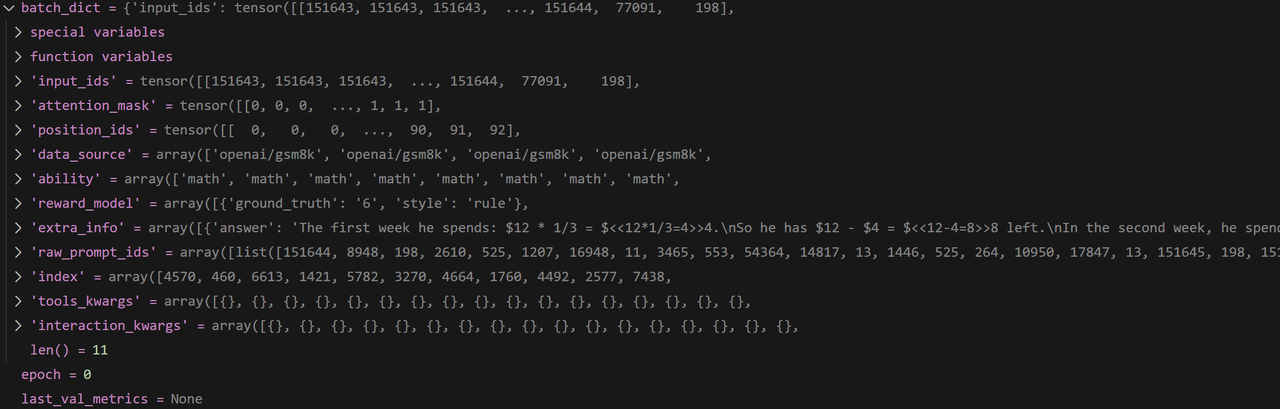
batch: DataProto = DataProto.from_single_dict(batch_dict)- 其获取到的batch_dict数据如下,可以看到其既包含原始数据,也包含了tokenizer处理后的数据,以及相关的attention_mask和position_ids等
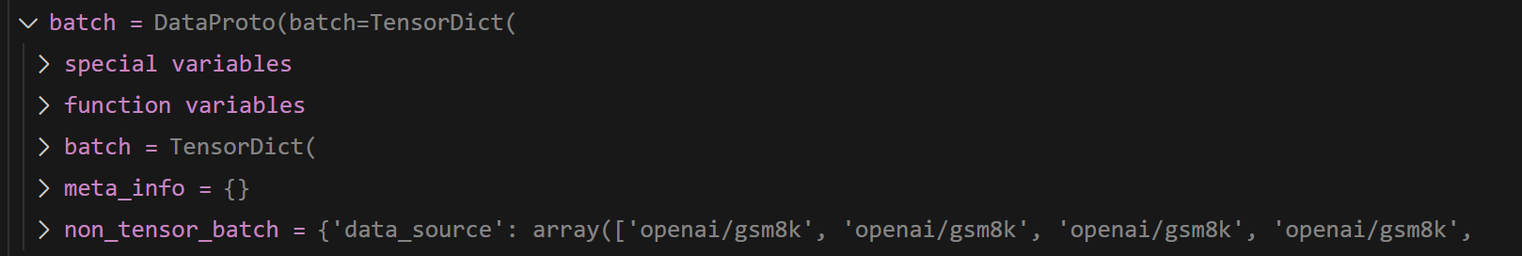
其后会进一步转换为的
DataProto类的batch,DataProto是Verl核心的数据处理类,其负责将tensor类型的变量转化为TensorDict,从而方便做到batch级的操作,如读取第几个batch的数据,或者将其切分为好几个小batch,还负责将非tensor内容放置到non_tensor_batch中。- 如下所示,tensor类型的变量包括了训练的核心数据
input_id、attention_mask、position_ids,非tensor类型的变量是一些额外的信息
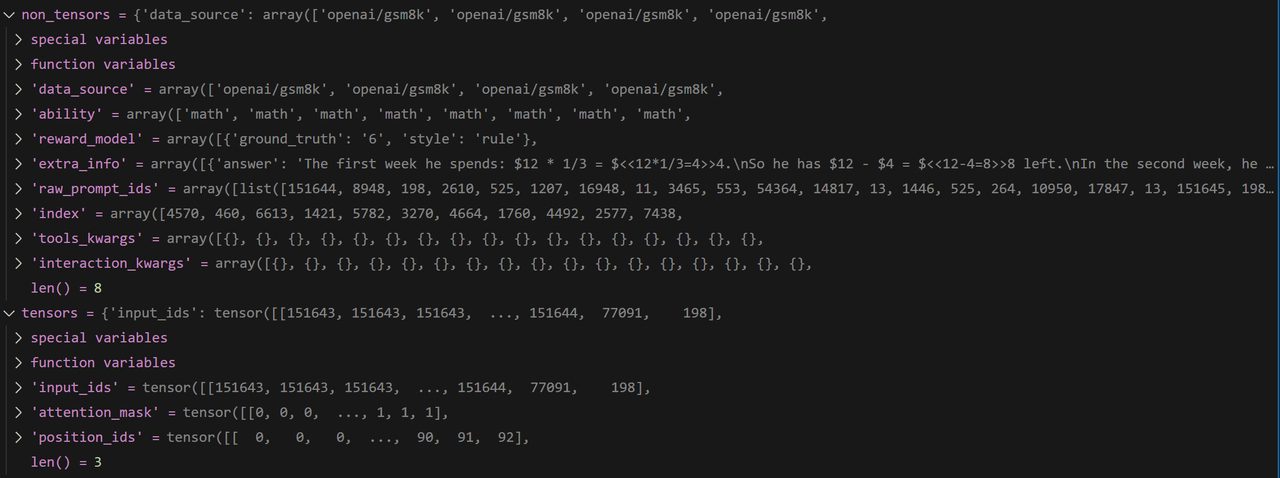
- 最终得到的
batch如下所示:
- 如下所示,tensor类型的变量包括了训练的核心数据
然后会从
batch中pop弹出获取到input_id、attention_mask、position_ids这3类数据并进一步组成DataProto类的gen_batch然后
gen_batch会被送给actor_rollout_wg然后在各个worker上执行generate_sequences来获取采样数据gen_batch_output注意
generate_sequences函数的dispatch方式是DP_COMPUTE_PROTO- 其分发方法为
dispatch_dp_compute_data_proto,相关代码如下,可以看到其将数据划分为了worker_group.world_size份,每一份后续才会作为worker的输入,worker在读取时如果这个数据在远程就会通过ray进行拉取。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50def dispatch_dp_compute_data_proto(worker_group, *args, **kwargs):
from verl.single_controller.base.worker_group import WorkerGroup
assert isinstance(worker_group, WorkerGroup)
# Note: enable auto padding for dp compute DatapProto
splitted_args, splitted_kwargs = _split_args_kwargs_data_proto_with_auto_padding(
worker_group.world_size,
*args,
**kwargs,
)
return splitted_args, splitted_kwargs
def _split_args_kwargs_data_proto_with_auto_padding(chunks, *args, **kwargs):
from verl.protocol import DataProto, DataProtoFuture
splitted_args = []
splitted_kwargs = {}
data_proto_len = None
padding_size = None
for arg in args:
assert isinstance(arg, (DataProto, DataProtoFuture))
if isinstance(arg, DataProto) and arg.is_padding_enabled():
# for padding, we only support DataProto with same length
if data_proto_len is None:
data_proto_len = len(arg)
padding_size = (chunks - (data_proto_len % chunks)) if (data_proto_len % chunks > 0) else 0
splitted_kwargs[_padding_size_key] = padding_size
else:
assert data_proto_len == len(arg), f"expecting all arg share same length of {data_proto_len}, but got {len(arg)}"
data_proto_len = len(arg)
arg.padding(padding_size=padding_size)
splitted_args.append(arg.chunk(chunks=chunks))
for key, val in kwargs.items():
assert isinstance(val, (DataProto, DataProtoFuture))
if isinstance(val, DataProto) and val.is_padding_enabled():
# for padding, we only support DataProto with same length
if data_proto_len is None:
data_proto_len = len(val)
padding_size = chunks - (data_proto_len % chunks)
splitted_kwargs[_padding_size_key] = padding_size
else:
assert data_proto_len == len(val), f"expecting all arg share same length of {data_proto_len}, but got {len(val)}"
data_proto_len = len(val)
splitted_kwargs[key] = val.chunk(chunks=chunks)
return splitted_args, splitted_kwargs- 其收集方法是
collect_dp_compute_data_proto,相关代码如下,可以看到其若采取的是sync模式,则输出会是DataProto类型,那么就直接将其拼接起来,如果是异步模式,即得到的是ray.ObjectRef类型,那么就只会将这些ref拼接起来。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35def collect_dp_compute_data_proto(worker_group, output):
import ray
from verl.protocol import DataProto
for o in output:
assert isinstance(o, (DataProto, ray.ObjectRef)), f"expecting {o} to be DataProto, but got {type(o)}"
output = collect_dp_compute(worker_group, output)
return _concat_data_proto_or_future(output)
def collect_dp_compute(worker_group, output):
from verl.single_controller.base.worker_group import WorkerGroup
assert isinstance(worker_group, WorkerGroup)
assert len(output) == worker_group.world_size
return output
def _concat_data_proto_or_future(output: List):
import ray
from verl.protocol import DataProto, DataProtoFuture
# make sure all the elements in output has the same type
for o in output:
assert type(o) is type(output[0])
o = output[0]
if isinstance(o, DataProto):
return DataProto.concat(output)
elif isinstance(o, ray.ObjectRef):
return DataProtoFuture.concat(output)
else:
raise NotImplementedError- 其分发方法为
并且
generate_sequences函数的执行模式是Execute.ALL,并且实例采用的是blocking模式,即会等其执行完后再把数据获取回来。
因为在
generate_sequences时一个输入可能会输出self.config.actor_rollout_ref.rollout.n个结果,所以为了对齐generate_sequences的结果,需要将batch中的数据对应重复self.config.actor_rollout_ref.rollout.n个,然后再合并gen_batch_output,此时batch中除了原本的input_id、attention_mask、position_ids外还有了prompt和responses、response_mask项prompt是在生成时额外在后续添加的提升内容,如
1
'system\nYou are Qwen, created by Alibaba Cloud. You are a helpful assistant.\nuser\nTom receives a $12 allowance per month. In the first week, he spends a third of it; in the second week, he spends a quarter of what he has left. How much money does he have left to finish the month? Let\'s think step by step and output the final answer after "####".\nassistant\n'- responsesh是实际模型生成的内容,如:
1
"To find out how much money Tom has left after the stipulated transactions, let's work through the steps:\n\n1. **Step 1: Tom receives $12 for his first allowance.**\n\n2. **Step 2: Tom spends a third of his allowance in the first week.**\n - Amount spent = $\\frac{1}{3} \\times $12 = $4$\n\n3. **Step 3: Calculate the remaining amount of money after spending in the first week:**\n - Remaining = $12 - $4 = $8\n\n4. **Step 4: Tom spends a quarter of what he has left in the second week.**\n - Amount spent in the second week = $\\frac{1}{4} \\times $8 = $2\n\n5. **Step 5: Calculate the remaining amount of money after spending in the second week:**\n - Remaining is $8 - $2 = $6\n\nSo, after he has both runs of spending, Tom has **$6** left to finish the month."如果有配置还会进行token级别的在各个DP rank间调整序列顺序以平衡计算量
然后会调用reward模型或者reward func来计算
reward,这使得batch中又额外添加了token_level_scores项还会按需使用actor重新计算
old_log_prob以避免actor与rollout的精度不统一,这使得batch中又额外添加了old_log_prob项如果配置了
use_reference_policy,还会计算ref的log_prob,使得batch中又额外添加了ref_log_prob项如果配置了
use_critic,还会调用critic计算values,使得batch中又额外添加了values元素然后会计算advantage,Verl支持GAE、GRPO等计算方式,计算后会给
batch添加advantages和returns项在PPO中
advantages就是优势,returns是advantages+values,policy loss 用advantages,value loss 用returns在GRPO中
advantages与returns相同
然后会更新critic,在更新critic过程中会使用到
batch的input_ids、responses、attention_mask、position_ids、values、returns其中会使用到
input_ids、responses、attention_mask、position_ids来在critic中重新前向传播得到最新预测的vpreds然后依据
vpredclipped = verl_F.clip_by_value(vpreds, values - cliprange_value, values + cliprange_value)计算clip后的value防止更新过猛进一步与returns比较得到loss
然后会更新actor,在更新actor过程中会会使用到
batch的input_ids、responses、attention_mask、position_ids、old_log_probs、advantages其中会使用到
input_ids、responses、attention_mask、position_ids来在actor中重新前向传播得到最新模型的log_prob,用于结合old_log_probs对advantages进行重要性采样然后使用经典的PPO clip来计算重要性采样下的advantage,从而更新actor
- 在训练过程中读取