【Verl源码分析(一)】Verl资源管理模式
注意查看的是0.4.1.x版本的Verl代码:https://github.com/verl-project/verl/tree/v0.4.1.x
任务与资源管理模式概览
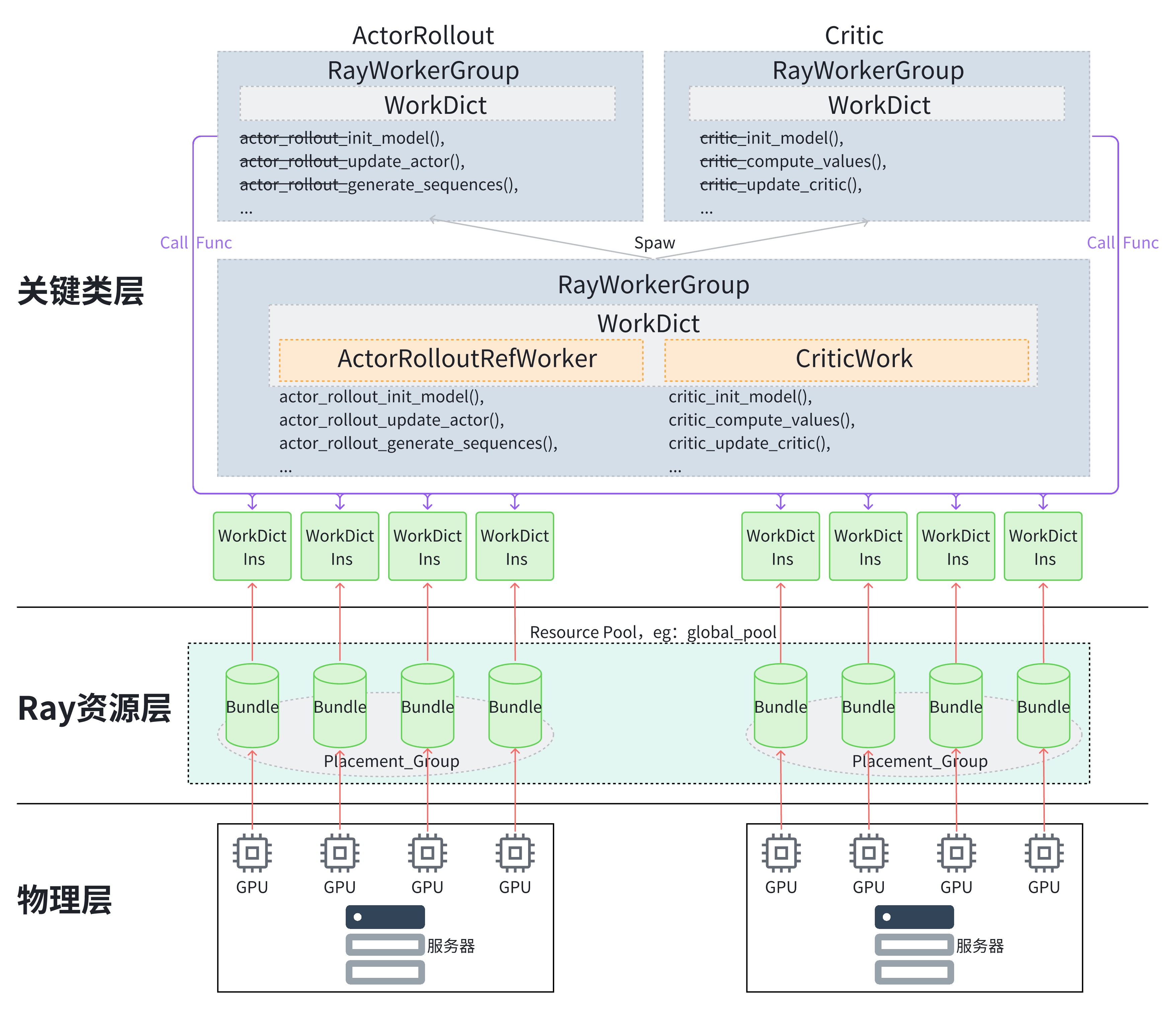
整体的概览图如上所示:
物理层:存在多个实际的服务器,假设每个服务器是同构的,即GPU数量相同。
Ray资源层:一个服务器对应一个
Placement_Group,一个GPU对应一个Bundle(Ray中程序运行的原子资源),多个Placement_Group组成了Resource Pool,Resource Pool内的资源含量由用户决定,在示例中多只存在一个Resource Pool,即global_pool,实际自行配置时可以设置多个Resource Pool,但是注意一个角色只应该在一个Resource Pool内。关键类层:
Verl会将一个
Resource Pool中放置的各个角色的类合并到WorkDict中,如图中的actor_rollout、critic,在合并时会用一个map记录各个角色与类的关系,然后各个角色的类的带MAGIC_ATTR属性的函数都会以{角色名}_{函数名}的命名方式保存在WorkDict中;然后其会用
RayWorkGroup来包裹WorkDict,在初始化RayWorkGroup时会在Resource Pool上生成多个WorkDict实例并将其存储在自身的workers属性中,Resource Pool中的每个Bundle对应一个实例,此外它还会重新生成WorkDict中各个带MAGIC_ATTR属性的函数,使得在相同的函数名在RayWorkGroup会先执行dispatch再执行execute_fn再执行collect,后面会专门介绍;但是实际使用不会用这个合并的
RayWorkGroup类去调用各个实例,而是会进一步按角色生成多个角色专属RayWorkGroup,各角色的RayWorkGroup也存在相同的workers属性来与实例管理并且也存在相同的函数,不同点在于其会额外将自身角色的函数名修改回来,从{角色名}_{函数名}修改为{函数名},这样这些RayWorkerGroup角色类就可以与原本的角色的类一样通过原函数名来调用。
RayWorkerGroup函数调用
WorkDict Ins是对WorkDict的ray actor的实例化,其有各个原角色类的初始化实例,如包含有”actor_rollout”角色的ActorRolloutRefWorker,包含”critic”角色的CriticWorker。其初始化时会遍历各个角色类中带MAGIC_ATTR属性的函数,将该函数以{角色名}_{函数名}的格式存储起来。代码如下所示。
1 | |
RayWorkGroup在初始化时会对WorkDict中带MAGIC_ATTR属性的函数进行进一步包装,其主要是根据MAGIC_ATTR属性获取dispatch_fn、collect_fn、execute_fn,然后将函数的执行使用func_generator包裹为先dispatch_fn广播参数,再调用execute_fn进行执行,最后使用collect_fn收集结果。代码如下所示。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92def _bind_worker_method(self, user_defined_cls, func_generator):
"""Binds worker methods to the WorkerGroup based on registered attributes.
Args:
user_defined_cls (type): The class containing methods to bind
func_generator (Callable): Function that generates the bound method
Returns:
List[str]: List of method names that were successfully bound
"""
method_names = []
for method_name in dir(user_defined_cls):
try:
method = getattr(user_defined_cls, method_name)
assert callable(method), f"{method_name} in {user_defined_cls} is not callable"
except Exception:
# if it is a property, it will fail because Class doesn't have instance property
continue
if hasattr(method, MAGIC_ATTR):
# this method is decorated by register
attribute = getattr(method, MAGIC_ATTR)
assert isinstance(attribute, Dict), f"attribute must be a dictionary. Got {type(attribute)}"
assert "dispatch_mode" in attribute, "attribute must contain dispatch_mode in its key"
dispatch_mode = attribute["dispatch_mode"]
execute_mode = attribute["execute_mode"]
blocking = attribute["blocking"]
# get dispatch fn
if isinstance(dispatch_mode, Dispatch):
# get default dispatch fn
fn = get_predefined_dispatch_fn(dispatch_mode=dispatch_mode)
dispatch_fn = fn["dispatch_fn"]
collect_fn = fn["collect_fn"]
else:
assert isinstance(dispatch_mode, dict)
assert "dispatch_fn" in dispatch_mode
assert "collect_fn" in dispatch_mode
dispatch_fn = dispatch_mode["dispatch_fn"]
collect_fn = dispatch_mode["collect_fn"]
# get execute_fn_name
execute_mode = get_predefined_execute_fn(execute_mode=execute_mode)
wg_execute_fn_name = execute_mode["execute_fn_name"]
# get execute_fn from string
try:
execute_fn = getattr(self, wg_execute_fn_name)
assert callable(execute_fn), "execute_fn must be callable"
except Exception:
print(f"execute_fn {wg_execute_fn_name} is invalid")
raise
# bind a new method to the RayWorkerGroup
func = func_generator(
self,
method_name,
dispatch_fn=dispatch_fn,
collect_fn=collect_fn,
execute_fn=execute_fn,
blocking=blocking,
)
try:
setattr(self, method_name, func)
method_names.append(method_name)
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError(f"Fail to set method_name {method_name}") from e
return method_names
def func_generator(self, method_name, dispatch_fn, collect_fn, execute_fn, blocking):
class Functor:
def __call__(this, *args, **kwargs):
args, kwargs = dispatch_fn(self, *args, **kwargs)
padding_count = kwargs.pop(_padding_size_key, 0)
output = execute_fn(method_name, *args, **kwargs)
if blocking:
output = ray.get(output)
output = collect_fn(self, output)
if padding_count > 0:
if isinstance(output, DataProto):
indices = [i for i in range(len(output))][:-padding_count]
output = output.select_idxs(indices)
elif isinstance(output, list):
output = output[:-padding_count]
return output
# use class type to pass the method_name to get a better observability
return type(method_name, (Functor,), {})()dispatch_fn、collect_fn:支持自定义也支持从默认提供的函数中获取,默认提供的有以下这些。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42DISPATCH_MODE_FN_REGISTRY = {
Dispatch.ONE_TO_ALL: {
"dispatch_fn": dispatch_one_to_all,
"collect_fn": collect_all_to_all,
},
Dispatch.ALL_TO_ALL: {
"dispatch_fn": dispatch_all_to_all,
"collect_fn": collect_all_to_all,
},
Dispatch.MEGATRON_COMPUTE: {
"dispatch_fn": dispatch_megatron_compute,
"collect_fn": collect_megatron_compute,
},
Dispatch.MEGATRON_PP_AS_DP: {
"dispatch_fn": dispatch_megatron_pp_as_dp,
"collect_fn": collect_megatron_pp_as_dp,
},
Dispatch.MEGATRON_PP_ONLY: {"dispatch_fn": dispatch_one_to_all, "collect_fn": collect_megatron_pp_only},
Dispatch.MEGATRON_COMPUTE_PROTO: {
"dispatch_fn": dispatch_megatron_compute_data_proto,
"collect_fn": collect_megatron_compute_data_proto,
},
Dispatch.MEGATRON_PP_AS_DP_PROTO: {
"dispatch_fn": dispatch_megatron_pp_as_dp_data_proto,
"collect_fn": collect_megatron_pp_as_dp_data_proto,
},
Dispatch.DP_COMPUTE: {"dispatch_fn": dispatch_dp_compute, "collect_fn": collect_dp_compute},
Dispatch.DP_COMPUTE_PROTO: {
"dispatch_fn": dispatch_dp_compute_data_proto,
"collect_fn": collect_dp_compute_data_proto,
},
Dispatch.DP_COMPUTE_PROTO_WITH_FUNC: {
"dispatch_fn": dispatch_dp_compute_data_proto_with_func,
"collect_fn": collect_dp_compute_data_proto,
},
Dispatch.DP_COMPUTE_METRIC: {"dispatch_fn": dispatch_dp_compute_data_proto, "collect_fn": collect_dp_compute},
Dispatch.DIRECT_ROLLOUT_METHOD: {
"dispatch_fn": dummy_direct_rollout_call,
"collect_fn": dummy_direct_rollout_call,
},
}- 这里专门将Dispatch.ONE_TO_ALL提出来查看,对于dispatch_fn其主要作用是将参数复制
world_size份,因为后面每个WorkDict Ins都会取对应位置的参数进行运行。这里复杂一些的策略会涉及到将数据切分给各个Ins以及如何收集各个Ins的结果等。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7def dispatch_one_to_all(worker_group, *args, **kwargs):
args = tuple([arg] * worker_group.world_size for arg in args)
kwargs = {k: [v] * worker_group.world_size for k, v in kwargs.items()}
return args, kwargs
def collect_all_to_all(worker_group, output):
return output- 这里专门将Dispatch.ONE_TO_ALL提出来查看,对于dispatch_fn其主要作用是将参数复制
execute_fn:预定义的fn有execute_all和execute_rank_zero,RayWorkerGroup类中相关实现如下所示。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10def get_predefined_execute_fn(execute_mode):
"""
Note that here we only asks execute_all and execute_rank_zero to be implemented
Leave the choice of how these two functions handle argument 'blocking' to users
"""
predefined_execute_mode_fn = {
Execute.ALL: {"execute_fn_name": "execute_all"},
Execute.RANK_ZERO: {"execute_fn_name": "execute_rank_zero"},
}
return predefined_execute_mode_fn[execute_mode]execute_all就是遍历各个worker(即WorkDict Ins)使用对应的参数来调用各个worker中对应的函数来执行。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62class RayWorkerGroup(WorkerGroup):
def execute_all(self, method_name: str, *args, **kwargs):
"""Alias for execute_all_async.
Args:
method_name: Name of the method to execute
*args: Positional arguments for the method
**kwargs: Keyword arguments for the method
Returns:
List of remote object references to the method executions
"""
return self.execute_all_async(method_name, *args, **kwargs)
def execute_all_async(self, method_name: str, *args, **kwargs):
"""Execute a method on all workers asynchronously.
Args:
method_name: Name of the method to execute
*args: Positional arguments for the method
**kwargs: Keyword arguments for the method
Returns:
List of remote object references to the method executions
"""
# Here, we assume that if all arguments in args and kwargs are lists,
# and their lengths match len(self._workers), we'll distribute each
# element in these lists to the corresponding worker
# print(f"execute_all_async: method {method_name}({args}, {kwargs})")
length = len(self._workers)
if all(isinstance(arg, list) for arg in args) and all(isinstance(kwarg, list) for kwarg in kwargs.values()):
if all(len(arg) == length for arg in args) and all(len(kwarg) == length for kwarg in kwargs.values()):
# print(f"splitting args and kwargs into {length} shards")
result = []
for i in range(length):
sliced_args = tuple(arg[i] for arg in args)
sliced_kwargs = {k: v[i] for k, v in kwargs.items()}
result.append(self._execute_remote_single_worker(self._workers[i], method_name, *sliced_args, **sliced_kwargs))
return result
return [self._execute_remote_single_worker(worker, method_name, *args, **kwargs) for worker in self._workers]
def _execute_remote_single_worker(self, worker, method_name: str, *args, **kwargs):
"""Execute a method on a single worker remotely.
Args:
worker: The worker actor handle
method_name: Name of the method to execute
*args: Positional arguments for the method
**kwargs: Keyword arguments for the method
Returns:
Remote object reference to the method execution
"""
if self.fused_worker_used and method_name not in self.method_names:
remote_call = getattr(worker, self.fused_worker_execute_fn_name)
return remote_call.remote(f"{self.sub_cls_name}_fwmn_{method_name}", *args, **kwargs)
# fused worker not used
remote_call = getattr(worker, method_name)
return remote_call.remote(*args, **kwargs)
execute_rank_zero就是顾名思义只在workers[0]中执行。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27class RayWorkerGroup(WorkerGroup):
def execute_rank_zero(self, method_name: str, *args, **kwargs):
"""Alias for execute_rank_zero_async.
Args:
method_name: Name of the method to execute
*args: Positional arguments for the method
**kwargs: Keyword arguments for the method
Returns:
Remote object reference to the method execution
"""
return self.execute_rank_zero_async(method_name, *args, **kwargs)
def execute_rank_zero_async(self, method_name: str, *args, **kwargs):
"""Execute a method on rank zero worker asynchronously.
Args:
method_name: Name of the method to execute
*args: Positional arguments for the method
**kwargs: Keyword arguments for the method
Returns:
Remote object reference to the method execution
"""
return self._execute_remote_single_worker(self._workers[0], method_name, *args, **kwargs)